What Animal Shares Most Dna With Humans
Dna
Through news accounts and crime stories, we're all familiar with the fact that the Deoxyribonucleic acid in our cells reflects each private's unique identity and how closely related nosotros are to ane another. The aforementioned is true for the relationships among organisms. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is the molecule that makes up an organism'south genome in the nucleus of every cell. It consists of genes, which are the molecular codes for proteins – the edifice blocks of our tissues and their functions. Information technology also consists of the molecular codes that regulate the output of genes – that is, the timing and caste of poly peptide-making. DNA shapes how an organism grows up and the physiology of its claret, bone, and brains.
DNA is thus particularly important in the written report of evolution. The corporeality of difference in Deoxyribonucleic acid is a examination of the difference between one species and another – and thus how closely or distantly related they are.
While the genetic difference betwixt individual humans today is minuscule – about 0.1%, on average – written report of the aforementioned aspects of the chimpanzee genome indicates a difference of about one.ii%. The bonobo (Pan paniscus), which is the close cousin of chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes), differs from humans to the same degree. The Deoxyribonucleic acid difference with gorillas, another of the African apes, is nigh 1.6%. Virtually importantly, chimpanzees, bonobos, and humans all show this same amount of difference from gorillas. A difference of 3.i% distinguishes us and the African apes from the Asian great ape, the orangutan. How exercise the monkeys stack up? All of the bully apes and humans differ from rhesus monkeys, for example, by near 7% in their Dna.
Geneticists have come up up with a variety of ways of calculating the percentages, which requite unlike impressions well-nigh how similar chimpanzees and humans are. The i.2% chimp-human distinction, for case, involves a measurement of only substitutions in the base building blocks of those genes that chimpanzees and humans share. A comparison of the entire genome, however, indicates that segments of Dna have as well been deleted, duplicated over and over, or inserted from i office of the genome into some other. When these differences are counted, there is an boosted 4 to v% distinction betwixt the man and chimpanzee genomes.
No matter how the adding is done, the large betoken still holds: humans, chimpanzees, and bonobos are more closely related to ane some other than either is to gorillas or any other primate. From the perspective of this powerful test of biological kinship, humans are not only related to the cracking apes – we are i. The Dna bear witness leaves us with i of the greatest surprises in biology: the wall between man, on the i mitt, and ape or beast, on the other, has been breached. The man evolutionary tree is embedded within the great apes.
The strong similarities between humans and the African bang-up apes led Charles Darwin in 1871 to predict that Africa was the likely identify where the man lineage branched off from other animals – that is, the place where the mutual ancestor of chimpanzees, humans, and gorillas once lived. The Deoxyribonucleic acid show shows an amazing confirmation of this daring prediction. The African dandy apes, including humans, have a closer kinship bail with one another than the African apes take with orangutans or other primates. Hardly e'er has a scientific prediction and so assuming, then 'out in that location' for its time, been upheld as the 1 made in 1871 – that human evolution began in Africa.
The DNA evidence informs this conclusion, and the fossils do, likewise. Even though Europe and Asia were scoured for early homo fossils long earlier Africa was even idea of, ongoing fossil discoveries confirm that the outset 4 1000000 years or and so of human being evolutionary history took identify exclusively on the African continent. Information technology is there that the search continues for fossils at or near the branching point of the chimpanzee and human lineages from our last mutual ancestor.
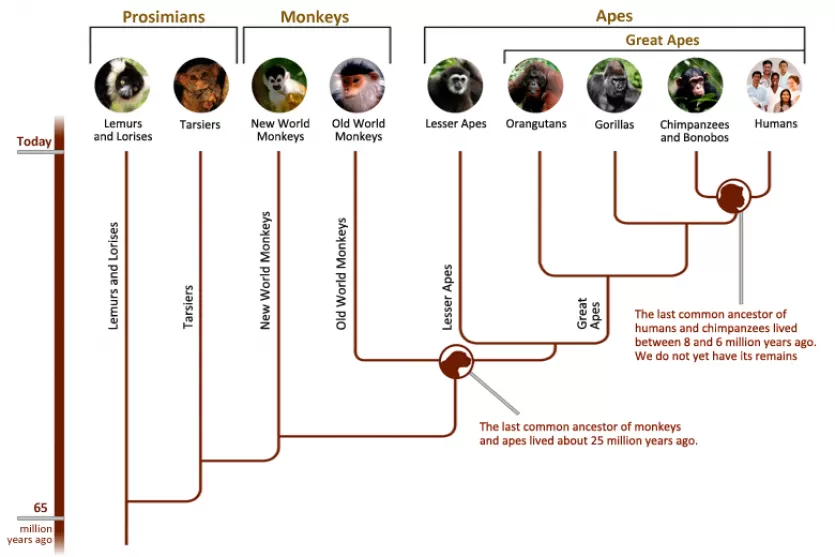
Primate Family Tree
Due to billions of years of evolution, humans share genes with all living organisms. The percentage of genes or DNA that organisms share records their similarities. Nosotros share more genes with organisms that are more closely related to us.
Humans vest to the biological grouping known as Primates, and are classified with the bully apes, one of the major groups of the primate evolutionary tree. Besides similarities in beefcake and behavior, our close biological kinship with other primate species is indicated by Deoxyribonucleic acid show. It confirms that our closest living biological relatives are chimpanzees and bonobos, with whom nosotros share many traits. Only nosotros did not evolve directly from whatsoever primates living today.
Deoxyribonucleic acid also shows that our species and chimpanzees diverged from a common antecedent species that lived between 8 and 6 million years ago. The last common ancestor of monkeys and apes lived about 25 one thousand thousand years ago.
Human Skin Color Variation
Ancient DNA and Neanderthals
I Species, Living Worldwide
Source: http://humanorigins.si.edu/evidence/genetics
Posted by: bridgesshen1994.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Animal Shares Most Dna With Humans"
Post a Comment